Kimberly-Little Chute Public Library calendar
Ranked by percentage change in circulation 2017-2018, high to low
Related posts:
Appleton Public Library. (8/27/2019)
Beaver Dam Community Library. (9/10/2019)
Beloit Public Library. (9/7/2019)
Brookfield Public Library. (9/3/2019)
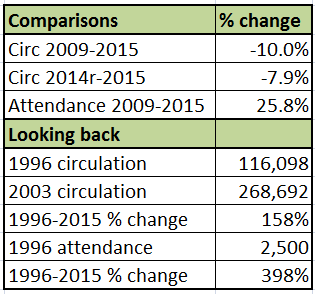
Brown County Public Library. (8/27/2019)
Cudahy Family Library. (9/12/2019)
Door County Library. (9/11/2019)
Eau Claire. L. E. Phillips Memorial Public Library. (9/1/2019)
Fitchburg Public Library. (9/10/2019)
Fond du Lac Public Library. (9/2/2019)
Franklin Public Library. (9/7/2019)
Janesville. Hedberg Public Library. (8/28/2019)
Kenosha Public Library. (8/29/2019)
La Crosse County Library. (9/6/2019)
La Crosse Public Library. (8/29/2019)
Madison Public Library. (8/26/2019)
Manitowoc Public Library. (9/4/2019)
Marathon County Public Library. (8/30/2019)
Marshfield. Everett Roehl Marshfield Public Library. (9/9/2019)
Menomonee Falls Public Library. (9/11/2019)
Menasha. Elisha D. Smith Public Library. (9/7/2019)
Middleton Public Library. (9/2/2019)
Milwaukee Public Library. (8/27/2019)
Mukwonago Community Library. (9/13/2019)
Neenah Public Library. (8/30/2019)
New Berlin Public Library. (9/11/2019)
Oshkosh Public Library. (8/31/2019)
Portage County Public Library. (9/8/2019)
Racine Public Library. (8/31/2019)
River Falls Public Library. (9/13/2019)
Sheboygan. Mead Public Library. (9/3/2019)
Shorewood Public Library. (9/10/2019)
Sun Prairie Public Library,. (9/4/2019)
Verona Public Library. (9/4/2019)
Watertown Public Library. (9/11/2019)
Waukesha Public Library. (8/28/2019)
Wauwatosa Public Library. (9/1/2019)
West Allis Public Library. (9/2/2019)
West Bend Community Memorial Library. (9/5/2019)
Whitefish Bay Public Library. (9/12/2019)
Wisconsin Rapids. McMillan Memorial Library. (9/5/2019)
10/28/2018 update starts here
Ranked in order by percentage change in annual program attendance from 2009 to 2017, plus to minus.
Source: Wisconsin Public Library Service Data (2015 preliminary)
Original 9/19/2015 post starts here.
Statistics found at Wisconsin Public Library Service Data: 1996 - Preliminary 2014. (Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction)
Related reading:
Parents, Children, and Libraries. (Pew Internet, 5/1/2013)
- Part 1: A profile of parents
- Demographic profile of a sample of parents vs. national parameters (table)
- Demographic profile of parents and other adults (table)
- Part 2: Parents and reading
- Reading frequency for parents and other adults (table)
- Types of books read in past 12 months differs for parents and other adults (column graph)
- Part 3: Parents and reading to children
- How often parents read to children, by age of youngest child (table)
- Characteristics of parents who read to their child every day (table)
- Parents say reading print books is very important to their children (pie graph)
- Part 4: Parents and libraries
- How important libraries are to individuals and their communities
- How important libraries are to parents
- How important are libraries (bar graph)
- Library use among parents and other adults (table)
- Characteristics of parents by library patronage (table)
- Recollection of library use by family members and experiences at libraries
- Overall library experiences are positive for almost all Americans (bar graph)
- Parents are more likely to have a library (bar graph)
- Changes in library use in recent years
- Changes in library use (bar graph)
- The main reasons parents' library use has increased in the past 5 years (table)
- Frequency of library visits, parents and other adults (bar graph)
- Activities at libraries
- What parents do at libraries (bar graph)
- How often people get help from library staff (bar graph)
- How helpful was library staff (bar graph)
- How much people know about what their library offers
- How much do you feel like you know about the different services and programs your public library offers? (bar graph)
- How much do parents know about the different services and programs the public library offers? (bar graph)
- Part 5: Parents, children and libraries
- Parents value libraries for their children
- Importance of libraries to parents (bar graph)
- How important are libraries for children (bar graph)
- Reason for importance of libraries (bar graph)
- Parents who say each is a MAJOR reason libraries are important (table)
- Library use by children (table)
- Frequency of children's visits to library in past 12 months (pie graph)
- Child's age makes a difference in how library is used (column graph)
- Parents' experiences (focus group responses)
- Community
- Responsibility (Several parents in our focus groups said that they wanted their children to use the library so that they could learn about personal responsibility, as well as how to act appropriately in public spaces.)
- Safety
Library Services in the Digital Age. (Pew Internet, 1/22/2013)
- Part 1: The role of libraries in people's lives and communities
- Family members' library use from childhood
- Did anyone else in your family use public libraries when you were growing up? (table)
- Americans' library use
- Have you ever visited a library or bookmobile in person? (table)
- Visited a library in-person in the last year? (table)
- A snapshot of Americans' library use habits (table)
- Experiences at public libraries are positive
- How important libraries are to individuals and their communities
- How important are libraries to you and your family?
- How important are libraries? (bar graph)
- Libraries' importance to the community as a whole
- How important are libraries? (table)
- Part 2: What people do at libraries and library websites
- Activities at libraries
- (bar graph)
- Browse the shelves for books or media
- Borrow print books
- Research topics that interest them
- Get help from a librarian
- Sit, read and study, or watch or listen to media
- Use a research database
- Attend or bring a younger person to a class, program, or event designed for children or teens
- Borrow a DVD or videotape of a movie or TV show
- Read or check out printed magazines or newspapers
- Attend a meeting of a group
- Attend a class, program or lecture for adults
- Borrow or download an audiobook
- Borrow a music CD
- How frequently people receive assistance from library staff
- (bar graph)
- by race/ethnicity
- by household income
- Use of library websites
- (table)
- Changes in library use in recent years
- The main reasons patrons' library use has changed in recent years (table)
- Technology users and library use
- Tech users more likely than non-tech users to say they use the library less than they used to (bar graph)
- Part 3: Technology use at libraries
- Those who have used free internet and computers in their communities (table)
- Use of computers and the internet at libraries
- Internet use at libraries (table)
- How important is free internet use at libraries?
- (table)
- Part 4: What people want from their libraries
- How much people know about what their libraries offer
- How much do you feel like you know about the different services and programs your public library offers? (bar graph)
- What is important for libraries to offer?
- What people think is important for libraries to offers? (bar graph)
- Blacks and Hispanics are more likely to see various library services as 'very important' (bar graph)
- Women are more likely than men to see various library services as 'very important' (bar graph)
- Examples
- Librarians to help people find information they need
- Borrowing books
- Free access to computers and the Internet
- Quiet study spaces for adults and children
- Programs and classes for children and teens
- Research resources such as free databases
- Job, employment, and career resources
- Free events and activities, such as classes and cultural events, for all ages
- Free public meeting spaces
- Public priorities for libraries
- What services and programs ;libraries should (and should not) implement (bar graph)
- Coordinate more closely with schools in providing resources to kids
- Offer free early literacy programs to help young children prepare for school
- Have completely separate locations or spaces for different services
- Have more comfortable spaces for reading, working, and relaxing at the library
- Offer a broader selection of e-books
- Offer more interactive learning experiences similar to museum exhibits
- Help users digitize materials such as family photos or historical documents
- Have most library service online so users can access them without having to visit the library
- Make most services automated
- Move some print books and stacks out of the library to free up more space
- The new services people say they would (and would not) use
- How likely American say they would be to use various library services (bar graph)
- Blacks and Hispanics are more likely to say they would use the following services (bar graph)
- Examples
- An online research service where you could post questions and get responses from librarians
- A program that allowed people to try out the newest tech devices or applications
- Personalized online accounts that give you customized recommendations for books and services based on your past library activity
- A cell phone app that allows you to access and use library services from your phone and see what programs the library offers
- Library kiosks located throughout the community where people can check out books, movies or music without having to go to the library itself
- A cell phone app that helps you locate material within the library by guiding you with GPS
- E-book readers already loaded with the book you want to read
- A digital media lab where you could create and upload new digital content like movies or your own e-books
- Classes on how to download e-books to handheld devices
- Classes or instruction on how to use handheld reading devices like e-book readers and tablet computers
- Part 5: The present and the future of libraries
- Libraries' strengths
- What should be libraries' 'guiding principle'?
- Things to change
- Library innovations
- Roadblocks and concerns
Reading & Library Habits in Different Communities. (Pew Research Center, 12/20/2012)
- Urban/Suburban/Rural
- Book readers
- Device owners
- Among e-book readers
- Purposes for reading
- Library activities
- Where people get book recommendations
Younger Americans’ Reading and Library Habits. (Pew Internet, 10/23/2012)
- General reading habits
- Book readers by age (graph)
- Book formats read in the past year, by age group (graph)
- E-books beyond e-readers (graph)
- How e-content has affected younger Americans' reading habits
- When to borrow, when to buy
- Thinking about the last book you read, in any format, did you... (graph)
- Library use
- Library use in the past year (table)
- How important is the public library to you and your family? (graph)
- How library patrons' habits have changed since they began borrowing e-books
- Library patrons' experiences with e-book borrowing
- How they find out about e-books
- The checkout process
- Non e-book borrowers
Libraries, patrons, and e-books. (Pew Internet, 6/22/2012)
- Part 1: An introduction to the issues surrounding libraries and e-books:
- The strained relationship between libraries and publishers
- The current state of play between libraries and publishers
- The rise of Amazon
- Part 2: Where patrons discover and get their books
- The way people prefer to get books in general: To buy or to borrow?
- Where did the most recent book come from?
- A closer look at libraries
- The e-book ecosystem: Where do e-book readers start their search?
- Part 3: Library users
- Demographics
- How important are libraries?
- Library users are more engaged with all kinds of reading
- Part 4: How people used the library in the past year
- Book-borrowing patterns
- Print books
- Audiobooks
- E-book borrowers
- Using the library for research
- Research resources and periodicals
- Get research help from a librarian
- Part 5: Libraries in transition
- How patrons' book-borrowing habits are changing
- Librarians: Changes in library holdings
- The changing role of librarians
- The move to e-books
- Staff training
- Patron training
- Part 6: A closer look at e-book borrowing
- Overview of responses in our online panel
- Checking out e-books
- How they find out about the process
- The checkout process
- Checking out e-books: The good, the bad, and Overdrive
- Selection of e-books in libraries
- Issues patrons have encountered
- Availability
- Waiting lists
- Compatibility
- Other issues
- The main things librarians hear
- How to improve the process for the future
- Librarians and publishers
- Part 7: Non-e-book borrowers
- Why not borrow e-books?
- Help and training from librarians